Six-Sigma is a complementary approach to improving processes. While they share the same tools, they have their own strengths and weaknesses. Six Sigma is a statistical process control technique. Lean starts with Lean's premise that a product must provide value, not just create it. Lean's key principle is to eliminate waste while improving the product's quality.
Problem solving regarding PDCA
Although there are differences in DMAIC problem solving and PDCA, they both use the DMAIC approach. The PDCA cycle requires more planning and analysis. PDCA, unlike DMAIC is not effective in solving urgent problems. This approach requires a lead problem-solver with technical skills. In the Six Sigma case, a problem-solving lead will be a "green belt" certified Six Sigma practitioner.
Six Sigma uses a cycle introduced by W. Edwards Deming in the 1950s to solve problems. It was intended to be used together with continuous improvement techniques to rebuild Japan’s industries. In the P stage (Plan), data must be gathered. Also, a clear mission must be established. After the PDCA stage, the team must decide on a recommended solution.

Process maps
One key difference between Six Sigma processes maps and Lean is the way each describes them. Both methods focus on defining the process in detail but each approach focuses more on different aspects. Lean, for example, focuses on mapping actual processes and not standard operating procedures. Consider the main activities, decisions, as well as sources of approval, when creating process mappings. Include areas that require multiple methods and factors. Match roles carefully and examine the flow of the process.
To show the flow of a process, a process map should contain steps, symbols and arrows. To ensure that each process accurately depicts the actual process, several people should review it. It should also contain information about the date and who to call if you have any questions. Overall process maps can help improve a process. However, they could be too complicated.
Analysis of cause and effect
Six Sigma, lean project management techniques are based on statistical analysis. The Cause and Effect Matrix or CAE is a method that links the outputs and inputs of a process. The customer's requirements are listed according to their importance. Outputs and inputs are ranked according the effect on the outcome. It is necessary to identify key process input variables and rank them.
While each technique has a unique set of benefits, they are not the same. Lean Six Sigma utilizes a process-improvement methodology that is based in Frederick Winslow Taylor’s Principles of Scientific Management. Taylor saw business processes as interconnected processes and workflows. He recommended reducing variability as well. Six-Sigma (and lean) are complementary in the effort to reduce waste.
Elimination of variation
Variability is an inevitable part of manufacturing processes. Variability can lead to uncertainty about the final outcome. Consistency is essential to provide professional results. Six Sigma and Lean manufacturing methods strive to eliminate variation. While some variation is acceptable, too much can lead to costly repairs and rework. It is important to determine the root causes of variation in order to address it.
First, look at the decision points to find variations. Process maps use diamonds to represent decision points. Six Sigma teams can begin by identifying decision points, and then start eliminating variations. This information is obtained from either the Six Sigma team owner or process owner. The Six Sigma group cannot focus on a process that is not governed by a standard process if it's owner. A process map might not work if the Six Sigma team lacks the technical capability to make necessary adjustments.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse?
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. With the rise of ecommerce, there is a greater demand for faster delivery times as well as more efficient processes.
Warehouses have to be flexible to meet changing requirements. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. The benefits of automating warehouses are numerous. Here are some benefits of investing in automation
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Boosts safety
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies scale more easily
-
Makes workers more efficient
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Minimizes downtime and increases uptime
-
High quality products delivered on-time
-
Eliminates human error
-
Helps ensure compliance with regulations
How can we increase manufacturing efficiency?
First, determine which factors have the greatest impact on production time. Then we need to find ways to improve these factors. If you don’t know how to start, look at which factors have the greatest impact upon production time. Once you've identified them, try to find solutions for each of those factors.
What are the goods of logistics?
Logistics refers to all activities that involve moving goods from A to B.
They encompass all aspects transport, including packaging and loading, transporting, storage, unloading.
Logisticians ensure that the product is delivered to the correct place, at the right time, and under safe conditions. Logisticians help companies improve their supply chain efficiency by providing information about demand forecasts and stock levels, production schedules, as well as availability of raw materials.
They can also track shipments in transit and monitor quality standards.
What skills is required for a production planner?
Production planners must be flexible, organized, and able handle multiple tasks. It is also important to be able communicate with colleagues and clients.
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. Forecasting and identifying production capacity are two key elements to this process.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
What do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes in order to learn more about Logistics?
No. It doesn't matter if you don't know anything about manufacturing before you learn about logistics. Knowing about manufacturing processes will help you understand how logistics works.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
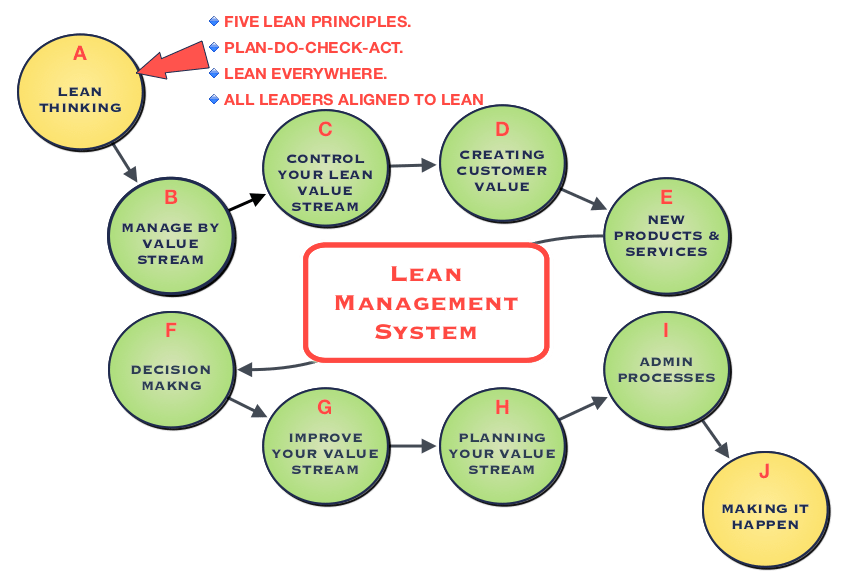
How to Use Lean Manufacturing for the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often defined as a set of principles used to improve the quality, speed, and cost of products and services. It emphasizes eliminating waste and defects throughout the value stream. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Lean manufacturing is widely used in many industries. Toyota's philosophy has been a key driver of success in many industries, including automobiles and electronics.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
With many benefits, lean manufacturing is becoming more common in the automotive industry. These include higher customer satisfaction, lower inventory levels, lower operating expenses, greater productivity, and improved overall safety.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three main types in lean manufacturing
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This strategy aims to decrease lead times, increase availability of parts and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This also applies to finished products that need minor repairs before being shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI: Continuous improvement aims to increase the efficiency of operations by constantly identifying and making improvements to reduce or eliminate waste. It involves continuous improvement of processes, people, and tools.