
Demand management is a technique that helps companies meet their customers' needs. It involves the ability to predict demand and bridge the gap between supply & marketing. The process can help companies improve the speed and quality of delivery, reduce the amount of invoice disputes, and lower the cost of running the business.
Companies that have a developed demand management process are more responsive to market shifts. This is because they have a system in place to identify the ideal customer, which can lead to effective marketing.
Businesses can use demand management to plan for future demand and improve customer satisfaction. When done correctly, it can help organizations reduce the number of invoice disputes and improve asset utilization. A solid demand management strategy is a good way to improve operational flexibility.
A project management program can improve the demand management approach. Such software can help teams coordinate their work and avoid siloed tasks. Also, a change management plan can help companies course correct supply chain problems quickly.
ILOG's PowerOps Suite combines manufacturing scheduling functions. Dynasys as well as QAD provide applications that allow organizations the ability to create and manage a demand/supply plan. These applications allow organizations to visualize the effects of changes on their supply chain. Optiant provides ERP solutions that allow organizations to establish efficient, consistent, and effective order- and supply management processes.
Real-Time Inventory, Terra Technology and CDC Software all offer real-time forecasting tools that can reduce supply-chain disruptions. Finally, the collaborative management strategy helps companies share information and resources. It incorporates performance indicators, knowledge-sharing, and planning for joint actions.
A few key factors should be considered before you decide to implement a strategy for demand management. These factors are helpful to professionals in understanding the process and focusing on the most critical aspects.
Leadership buy-in and support is crucial for demand management. This is because demand management is a highly collaborative process that involves various levels of management. Managers and top executives are the most important players at the highest levels. They are responsible for ensuring all members are on the exact same page. Important to the success and sustainability of the initiative are those at the bottom.
There are many applications available that can assist organizations in implementing a demand/supply planning. However, these key points should be kept in mind.

Understanding the market and identifying the ideal customer is key to demand management. An organization must be able to accurately measure and analyze the outcomes of its efforts, in addition to knowing which customers to target.
Businesses need to be more agile in order to develop a demand management plan that is easily adaptable to changing circumstances. An effective plan can decrease supply chain disruptions, tactical forecast error, and supply chain disruptions. Demand management can be used to develop and implement strategic and portfolio plans.
FAQ
What does it take for a logistics enterprise to succeed?
You need to have a lot of knowledge and skills to manage a successful logistic business. Good communication skills are essential to effectively communicate with your suppliers and clients. You should be able analyse data and draw inferences. You must be able to work well under pressure and handle stressful situations. You must be creative and innovative to develop new ideas to improve efficiency. To motivate and guide your team towards reaching organizational goals, you must have strong leadership skills.
It is important to be organized and efficient in order to meet tight deadlines.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. E-commerce has increased the demand for quicker delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses should be able adapt quickly to new needs. Technology is essential for warehouses to be able to adapt quickly to changing needs. Automating warehouses has many benefits. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety enhancements
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
This allows companies to scale easily
-
It makes workers more efficient
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
Quality products delivered on time
-
Removing human error
-
It ensures compliance with regulations
What are the 7 Rs of logistics.
The acronym "7R's" of Logistics stands for seven principles that underpin logistics management. It was developed by the International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL) and published in 2004 as part of its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The following letters make up the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable - have confidence in the ability to deliver on commitments made.
-
Reasonable - make sure you use your resources well and don't waste them.
-
Realistic – Consider all aspects, including cost-effectiveness as well as environmental impact.
-
Respectful - show respect and treat others fairly and fairly
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable: Provide customers with value-added service
What are manufacturing and logistic?
Manufacturing refers to the process of making goods using raw materials and machines. Logistics manages all aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning and distribution, inventory control, transportation, customer service, and transport. Manufacturing and logistics can often be grouped together to describe a larger term that covers both the creation of products, and the delivery of them to customers.
Are there ways to automate parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The wheel was invented by the Egyptians thousands of years ago. We now use robots to help us with assembly lines.
Robotics is used in many manufacturing processes today. These include:
-
Robots for assembly line
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots create products
Manufacturing can also be automated in many other ways. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was developed in Japan during the 1970s and 1980s by Taiichi Ohno, who received the Toyota Production System (TPS) award from TPS founder Kanji Toyoda. Michael L. Watkins published the first book on lean manufacturing in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often described as a set if principles that help improve the quality and speed of products and services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing emphasizes reducing non-value-added activities like inspection, rework and waiting.
Lean manufacturing not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. Companies can also achieve their goals faster by reducing employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy, for example, is what has enabled it to be successful in electronics, automobiles, medical devices, healthcare and chemical engineering as well as paper and food.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value- Identify the added value your company brings to society. What makes you stand out from your competitors?
-
Reduce Waste - Eliminate any activity that doesn't add value along the supply chain.
-
Create Flow: Ensure that the work process flows without interruptions.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Develop Relationships: Establish personal relationships both with internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing isn’t new, but it has seen a renewed interest since 2008 due to the global financial crisis. Many businesses are now using lean manufacturing to improve their competitiveness. Economists think that lean manufacturing is a crucial factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These benefits include increased customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels and lower operating costs.
Lean manufacturing can be applied to almost every aspect of an organization. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
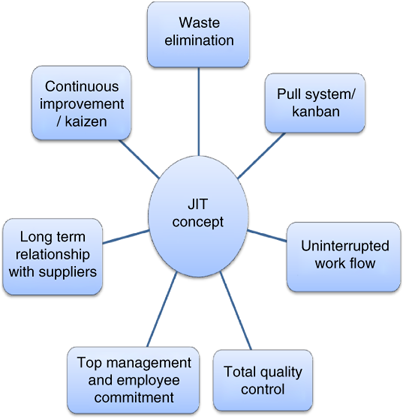
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT is a method in which components are assembled right at the moment of use, rather than being manufactured ahead of time. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI),: Continuous improvement aims improve the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by continuously identifying issues and making changes to reduce waste. Continuous improvement refers to continuous improvement of processes as well people and tools.